Terpenes and Terpenoids

Terpenes and terpenoids are often used interchangeably. Though the two are closely related, they are not one and the same thing. Here is the ultimate guide on terpenes and terpenoids; what they are, how they differ, and the therapeutic benefits that have brought them on the radar lately.
Terpenes and terpenoids are similar in many ways. Terpenes are more popular than terpenoids. However, what most people refer to as terpenoids are actually terpenes. Once you have understood the difference between the two, it will be clear why in some instances, such as when discussing the therapeutic benefits, it is “okay” to use the two terms interchangeably.
What is the difference between terpenes and terpenoids?
Terpenes are essential aromatic oils that are dominant in most cannabis strains. They are biosynthesized from acetyle-CoA or a glycolytic intermediate. Terpenoids are terpenes that have undergone oxidation through drying and curing.
Terpenoids, also called isoprenoids, are a diverse lipid group that are similar to terpenes. While terpenes contain a hydroxyl group terpenoids contain additional functional units that make them unique. Terpenoids may also be referred to as terpenes that have been chemically modified.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are arguably the most diverse class of natural products. Cannabis plants have more than 200 terpenes that have been identified, though only a handful have been studied.
Most terpenes are found in plants. However, larger and more complex terpenes (such as squalene and lanosterol) may be found in animals. Terpenes are made up of isoprene units and usually have these units in multiples of five.
Terpenes are found in the resinous glands on cannabis buds and flowers together with phytocannabinoids. The term terpene when used correctly refers to the number (in multiples) of isoprene units found in a compound. When used loosely (as in terpenoids) it refers to the additional functional units in the skeletal isoprene units.
What Are Terpenoids?
Terpenoids can be defined as terpenes that have additional functional groups that give them unique characteristics. Terpenoids may also be defined as terpenes that have undergone oxidation through the process of drying and curing.
Here are the common types of terpenoids:
Common Marijuana Terpenes & Their Health Benefits
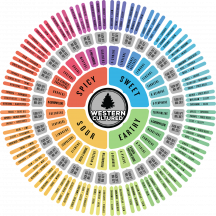
Modern research has shown that a comprehensive terpene wheel (see below) has over 20,000 terpene types; the cannabis plant has about 200 terpenes. Science is only beginning to catch up on the diverse mechanisms and potential benefits of this group of compounds.
Here are the common terpenes found in cannabis and the therapeutic benefits that they have to offer.
Myrcene
Myrcene is a monoterpene whose aroma has been described as earthy or herbal. This terp is also found in oil of hops, bay leaves, wild thyme, lemon grass and many other plants.
Myrcene lowers the blood- brain barrier resistance and allows itself and other terpenes to cross to the brain. In the case of cannabinoids, myrcene increases their speed of action in that their effects are felt faster. It also increases the maximum saturation level of the CB1 receptor, increasing the psychoactive benefits of THC.
Myrcene also offers analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimutagenic benefits.
Pinene
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpenoid which has the aroma of pine and fir. α-pinene and β-pinene are the common forms of pinene occurring in cannabis, they are terpenoids. Pinene is also found in balsamic resin and pine wood. It has anti-inflammatory, expectorant and bronchodilator properties. It has also been used as an anti-cancer agent in Chinese medicine.
Limonene
Limonene is a monocyclic monoterpenoid with a strong citrusy smell. It is also found in citrus fruit rinds, juniper, rosemary and pine needle oils. It is absorbed easily into the bloodstream and also improves the absorption of other terpenes. It has potent antibacterial and antifungal benefits. It has shown potential in the suppression of breast cancer as well.
Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene that is also found in basils, cloves, black pepper, and lavender. It has a peppery or woody aroma. Caryophyllene is the only terpene that interacts directly with the endocannabinoid system through the CB2 receptors. It offers antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties against neuropathic pain.
Linalool
Linalool is a non-cyclic monoterpenoid that has floral and lavender undertones. It is commonly used in aromatherapy to provide relaxation and anti-anxiety effects. It also improves immunity and has been used in the treatment of lung inflammation.
Camphene
Camphene is a plant-derived monoterpene with the odor of damp woodlands and fir needles. Recent research has shown that camphene may help in treating cardiovascular disease. In a rat model, this terpene helped to reduce plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Terpineol
α-Terpineol is common in cannabis strains that have high pinene levels. It has antioxidant and antimalarial properties.
Phellandrene
Phellandrene is a terpene that smells of peppermint. It has been used in Chinese medicine to relieve digestion problems. It is one of the easiest terpenes to identify in a lab setting. It is easily absorbed through the skin which makes it ideal for use in topical products. It is also found in herbs and spices such as garlic, dill, and parsley.
Carene
Delta-3-carene is a bicyclic monoterpene with a mix of pungent-sweet odor. It is commonly found in essential oils such as cypress oil, juniper berry oil and fir needle oils. It depresses the central nervous system and may be used to dry out excess body fluids in tears and sweat. It is also found in bell peppers and citrus peels.
Humulene
Humulene is a sesquiterpene found in cannabis in the form of α-humulene and α–caryophyllene which is an isomer of β–caryophyllene. It is common in hops and cannabis sativa strains. Humulene offers anti-tumor, anti-bacterial, and appetite suppressing benefits. It has been used to facilitate weight loss.
Pulegone
Pulegone is a monocyclic monoterpenoid which is found in cannabis but is abundant in rosemary. It offers sedative and fever-reducing benefits. It also helps to alleviate the short-term memory loss associated with high levels of THC. It can also be used as an insecticide.
Sabinene
Sabinene is a bicyclic monoterpene which is common in cannabis, Norway Spruce, black pepper, and basil. Preliminary research has shown that this terpene can offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Are Terpenes in Cannabis Psychoactive?
Terpenes lack psychoactive properties and will therefore not get you high. On the contrary, some terpenes may diminish the psychoactive effects of THC.
How do I isolate terpenes during cannabis extractions?
Terpenes, as well as terpenoids, are degraded easily by heating. Consequently they need to be isolated in the first part of extraction and stored away in air and light-tight containers to prevent degradation. After the cannabinoids have been separated the terpenes can be added back to boost the therapeutic benefits through cannabis synergy.
What are Cannabis Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis, as well as other plants, that provide the different pigments. Cannabis has over 20 known flavonoids including anthocyanin, apigenin, quercetin, cannflavin A and cannflavin B (unique to cannabis), and kaempferol. Flavonoids offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits and also boost the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids though cannabis synergy.
What is a Terpene Wheel?
It’s a graphical representation, in the form of a cyclic wheel, which shows the natural occurring terpenes, their unique characteristics, and where they are commonly found.
Terpenes and terpenoid are an essential component of cannabinoid therapy; we will keep updating this definitive guide as the body of research in this area continues to expand.
Link to Original Article

 cannabisreports.org
cannabisreports.org

Terpenes and terpenoids are often used interchangeably. Though the two are closely related, they are not one and the same thing. Here is the ultimate guide on terpenes and terpenoids; what they are, how they differ, and the therapeutic benefits that have brought them on the radar lately.
Terpenes and terpenoids are similar in many ways. Terpenes are more popular than terpenoids. However, what most people refer to as terpenoids are actually terpenes. Once you have understood the difference between the two, it will be clear why in some instances, such as when discussing the therapeutic benefits, it is “okay” to use the two terms interchangeably.
What is the difference between terpenes and terpenoids?
Terpenes are essential aromatic oils that are dominant in most cannabis strains. They are biosynthesized from acetyle-CoA or a glycolytic intermediate. Terpenoids are terpenes that have undergone oxidation through drying and curing.
Terpenoids, also called isoprenoids, are a diverse lipid group that are similar to terpenes. While terpenes contain a hydroxyl group terpenoids contain additional functional units that make them unique. Terpenoids may also be referred to as terpenes that have been chemically modified.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are arguably the most diverse class of natural products. Cannabis plants have more than 200 terpenes that have been identified, though only a handful have been studied.
Most terpenes are found in plants. However, larger and more complex terpenes (such as squalene and lanosterol) may be found in animals. Terpenes are made up of isoprene units and usually have these units in multiples of five.
| Terpene | Isoprene Units |
| Monoterpenes | 2 |
| Sesquiterpenes | 3 |
| Diterpenes | 4 |
| Sesterterpenes | 5 |
| Triterpenes | 6 |
Terpenes are found in the resinous glands on cannabis buds and flowers together with phytocannabinoids. The term terpene when used correctly refers to the number (in multiples) of isoprene units found in a compound. When used loosely (as in terpenoids) it refers to the additional functional units in the skeletal isoprene units.
What Are Terpenoids?
Terpenoids can be defined as terpenes that have additional functional groups that give them unique characteristics. Terpenoids may also be defined as terpenes that have undergone oxidation through the process of drying and curing.
Here are the common types of terpenoids:
| Terpenoid | Isoprene Skeletal Units |
| Hemiterpenoid | 1 |
| Monoterpenoid | 2 |
| Sesquiterpenoid | 3 |
| Diterpenoid | 4 |
| Sesteterpenoid | 5 |
| Triterpenoid | 6 |
| Tetraterpenoid | 8 |
| Politerpenoid | N |
Common Marijuana Terpenes & Their Health Benefits
Modern research has shown that a comprehensive terpene wheel (see below) has over 20,000 terpene types; the cannabis plant has about 200 terpenes. Science is only beginning to catch up on the diverse mechanisms and potential benefits of this group of compounds.
Here are the common terpenes found in cannabis and the therapeutic benefits that they have to offer.
Myrcene
Myrcene is a monoterpene whose aroma has been described as earthy or herbal. This terp is also found in oil of hops, bay leaves, wild thyme, lemon grass and many other plants.
Myrcene lowers the blood- brain barrier resistance and allows itself and other terpenes to cross to the brain. In the case of cannabinoids, myrcene increases their speed of action in that their effects are felt faster. It also increases the maximum saturation level of the CB1 receptor, increasing the psychoactive benefits of THC.
Myrcene also offers analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimutagenic benefits.
Pinene
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpenoid which has the aroma of pine and fir. α-pinene and β-pinene are the common forms of pinene occurring in cannabis, they are terpenoids. Pinene is also found in balsamic resin and pine wood. It has anti-inflammatory, expectorant and bronchodilator properties. It has also been used as an anti-cancer agent in Chinese medicine.
Limonene
Limonene is a monocyclic monoterpenoid with a strong citrusy smell. It is also found in citrus fruit rinds, juniper, rosemary and pine needle oils. It is absorbed easily into the bloodstream and also improves the absorption of other terpenes. It has potent antibacterial and antifungal benefits. It has shown potential in the suppression of breast cancer as well.
Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene that is also found in basils, cloves, black pepper, and lavender. It has a peppery or woody aroma. Caryophyllene is the only terpene that interacts directly with the endocannabinoid system through the CB2 receptors. It offers antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties against neuropathic pain.
Linalool
Linalool is a non-cyclic monoterpenoid that has floral and lavender undertones. It is commonly used in aromatherapy to provide relaxation and anti-anxiety effects. It also improves immunity and has been used in the treatment of lung inflammation.
Camphene
Camphene is a plant-derived monoterpene with the odor of damp woodlands and fir needles. Recent research has shown that camphene may help in treating cardiovascular disease. In a rat model, this terpene helped to reduce plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Terpineol
α-Terpineol is common in cannabis strains that have high pinene levels. It has antioxidant and antimalarial properties.
Phellandrene
Phellandrene is a terpene that smells of peppermint. It has been used in Chinese medicine to relieve digestion problems. It is one of the easiest terpenes to identify in a lab setting. It is easily absorbed through the skin which makes it ideal for use in topical products. It is also found in herbs and spices such as garlic, dill, and parsley.
Carene
Delta-3-carene is a bicyclic monoterpene with a mix of pungent-sweet odor. It is commonly found in essential oils such as cypress oil, juniper berry oil and fir needle oils. It depresses the central nervous system and may be used to dry out excess body fluids in tears and sweat. It is also found in bell peppers and citrus peels.
Humulene
Humulene is a sesquiterpene found in cannabis in the form of α-humulene and α–caryophyllene which is an isomer of β–caryophyllene. It is common in hops and cannabis sativa strains. Humulene offers anti-tumor, anti-bacterial, and appetite suppressing benefits. It has been used to facilitate weight loss.
Pulegone
Pulegone is a monocyclic monoterpenoid which is found in cannabis but is abundant in rosemary. It offers sedative and fever-reducing benefits. It also helps to alleviate the short-term memory loss associated with high levels of THC. It can also be used as an insecticide.
Sabinene
Sabinene is a bicyclic monoterpene which is common in cannabis, Norway Spruce, black pepper, and basil. Preliminary research has shown that this terpene can offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Are Terpenes in Cannabis Psychoactive?
Terpenes lack psychoactive properties and will therefore not get you high. On the contrary, some terpenes may diminish the psychoactive effects of THC.
How do I isolate terpenes during cannabis extractions?
Terpenes, as well as terpenoids, are degraded easily by heating. Consequently they need to be isolated in the first part of extraction and stored away in air and light-tight containers to prevent degradation. After the cannabinoids have been separated the terpenes can be added back to boost the therapeutic benefits through cannabis synergy.
What are Cannabis Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis, as well as other plants, that provide the different pigments. Cannabis has over 20 known flavonoids including anthocyanin, apigenin, quercetin, cannflavin A and cannflavin B (unique to cannabis), and kaempferol. Flavonoids offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits and also boost the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids though cannabis synergy.
What is a Terpene Wheel?
It’s a graphical representation, in the form of a cyclic wheel, which shows the natural occurring terpenes, their unique characteristics, and where they are commonly found.
Terpenes and terpenoid are an essential component of cannabinoid therapy; we will keep updating this definitive guide as the body of research in this area continues to expand.
Link to Original Article

Terpenes and Terpenoids: The Ultimate Guide - CannabisReports.org
Here is the ultimate guide on terpenes and terpenoids; what they are, how they differ, and the therapeutic benefits that have brought them on the radar lately.